What is the endocannabinoid system?

The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cellular signaling system in the body that plays an important role in regulating various physiological processes in the body. This system consists of endocannabinoids, which are molecules produced by the body, and the receptors to which these molecules bind. These receptors are found on the surfaces of cells throughout the body. The two main endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). ECS regulates body processes such as: appetite, pain sensation, mood and memory. It also helps maintain balance in the body. ECS dysregulation is associated with a variety of health problems, including chronic pain, anxiety, and depression.
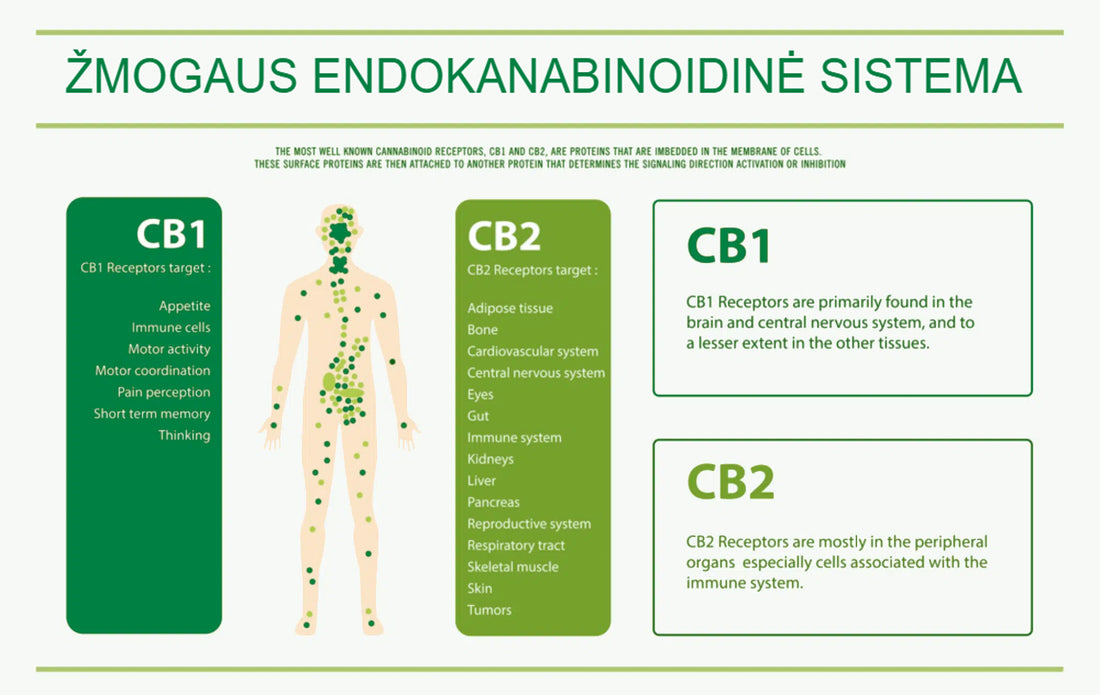
The main receptor types in the endocannabinoid system are the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
1) CB1 receptors are mainly found in the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. Here they play an important role in the body. CB1 receptors regulate mood, appetite, pain perception and memory. They are also found in other parts of the body, such as the liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
2) CB2 receptors are primarily found in the immune system, including the spleen, thymus, and white blood cells. CB2 receptors regulate inflammation and immune response. They are also found in other parts of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract and the peripheral nervous system.
Both CB1 and CB2 receptors bind to endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids, which are found in the hemp plant molecules such as THC and CBD. THC binds to the CB1 receptor and takes the position of our biological endocannabinoid called "anandamide" and is thus able to affect our psyche. Meanwhile, CBD binds to CB2 receptors and is able to reduce inflammation, anxiety and calm the nervous system.
